Embarking on the journey of cryptocurrency investment can be thrilling, yet complex. To help you navigate these turbulent waters, we've prepared a comprehensive guide to crypto staking. This guide is carefully broken down into digestible parts, each covering a unique aspect of staking.
From understanding basic terminology, to exploring the mechanics of staking, its benefits and risks, and even how to choose the right cryptocurrency for staking, we've got you covered. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a novice venturing into the realm of digital currencies, this guide will serve as your roadmap to successful crypto staking. Read on!
Learn more about crypto staking and get started with this investing modality that is taking up the center stage in the crypto world.
Much like other concepts in the crypto universe, staking can be a simple or complex idea depending on how much one understands blockchain technology and its mechanisms. Getting to know staking a little deeper can prove helpful for investors and traders, as this process is one more way to earn money with crypto.
With crypto staking, you can receive rewards by supporting a token as you lock yourself out of selling it for some time. In this article, we'll go through the whole process of staking and teach how to do it. Come along!
What Is Crypto Staking, and how Does it Work?
In short, crypto staking means locking up a number of coins for some time to earn a percentage-rate revenue over time. It has become one of the most popular types of crypto investment over the past few years, especially for newbie investors that need to start with less complex investments.
How does staking in crypto work?
Crypto staking is a process when an investor stakes their coins (freeze it on the crypto wallet) and the network is able to use these holdings to forge new blocks on the blockchain. If you stake more crypto you will receive more odds.

Why Staking is Important for Blockchain?
Let's take a step back and understand the technical structure behind staking.
As blockchains are decentralized networks, there are no intermediaries or well-known institutions to analyze and validate new activity across the chain. Instead, some networks use an unchangeable historical record of blocks of recent transactions to prevent fraud and errors. This process is called the Proof of Stake consensus mechanism.
Proof of Stake or PoS algorithm arose as an alternative for the Proof of Work security method, an energy-intensive process that requires users to contribute with computer power. PoS is proving to be more energy-efficient to all the networks adopting this new approach.
Staking happens when users create a new block or vote to accept a proposed one, as they have to put some of their own assets at risk. However, if the block is accepted, the stakers will receive percentage-rated interest over time through transaction fees. The more is at stake, the higher are the chances of receiving a great reward.
However, not all cryptocurrencies use PoS. Like Bitcoin, some networks still use PoW as their consensus mechanism and can't be staked. Because of that, it is essential to check if it allows staking before purchasing it for investment interests.
Benefits and Risks of Staking Crypto
For some investors, staking can generate some passive income while also contributing to the security of a network, making it more resistant to attacks.
Staking offers a higher annual percentage yield than a traditional savings account and presents less risk than other crypto investing modalities. It doesn't require the investor to have advanced computing equipment and has a limited environmental footprint compared to the PoW mining process.
Nonetheless, staking has its risks, like any other type of investment. This process is at the mercy of the market, meaning that if the APY is high, but the staked cryptocurrency decreases in value over the year, the investor is still losing.
There is also the lockup and rewards duration factor. Staking often requires a lockup period where investors can't move their crypto. For example, if the coin increases in value but is staked, the investor can't trade it. At the same time, the staking rewards also take a long time to be distributed, as some staking assets don't allocate the rewards daily.
How to Stake Crypto
You now know what staking is, how it works, and its pros and cons. If you want to start making a profit from this method, now is the time! Here you'll learn the step-by-step to stake your coins on the BullPerks platform:
1. Buy BLP tokens and transfer them to your wallet
As stated before, you need to buy a stakable cryptocurrency, in this case, BLP tokens. You can purchase BLP on supported centralized exchanges as well as decentralized ones and transfer it to your MetaMask wallet.
Learn more about how to purchase BLP tokens here.
2. Log into your BullStarter account
If you are already registered on the BullStarter platform, you can log in and proceed to the Pools > Staking Pools page. If not, you need to register and complete the Know Your Customer procedure.
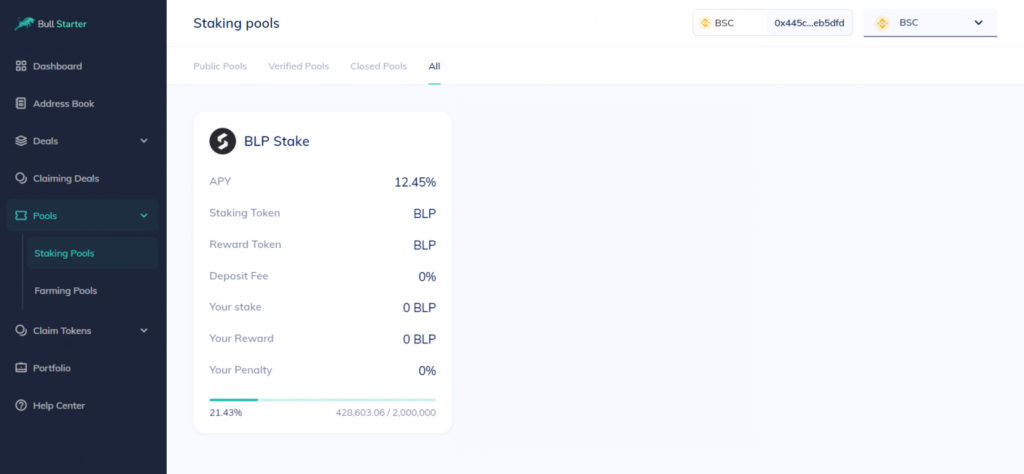
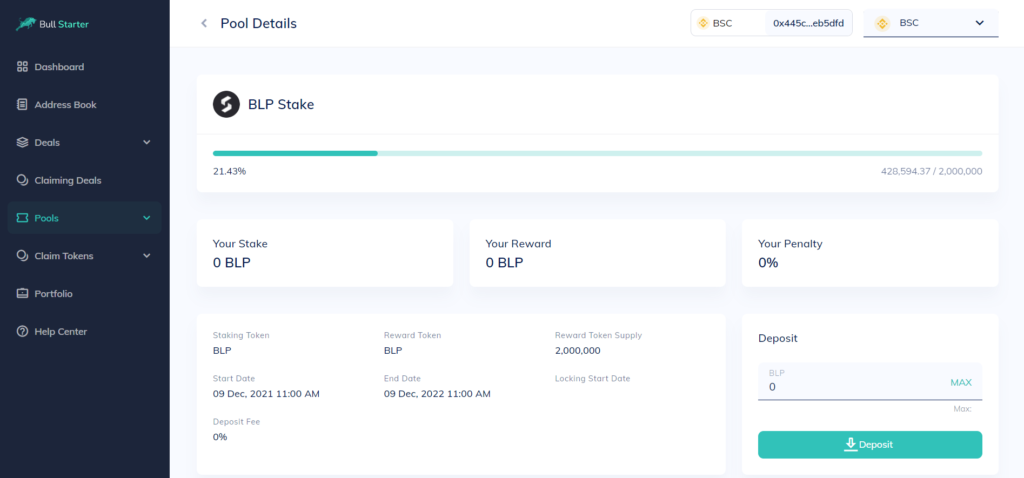
3. Join a staking pool
On the Staking Pools page, you'll be able to see all the available pools. Choose a pool and click on Deposit to type in the number of tokens you want to stake. Approve and confirm the operation, click on Deposit and confirm the transaction again.
Congrats! You have staked your coins with BullPerks! Now you can check your investment on the Your Stake dashboard.
Risks of staking crypto in short words:
But let is see in the details:
Top 5 risks to understand before staking cryptocurrency
While staking may present higher earnings compared to conventional passive income investment approaches, it also carries inherent risks. It's prudent to acquaint yourself with the hazards of staking, and to aid in this, we have compiled the most notable risks for your attention. Take a look!
1. Impermanent loss
The cryptocurrency market is intrinsically extremely volatile, which implies that token values can sway drastically within a few hours. When staking, individuals contribute liquidity to the pool, which can be distressing if the value of the staked coin diminishes during the staking duration, as this could lead to substantial financial loss.
2. Crypto token lockup periods
Throughout the term of your staking, the funds you've staked will be locked and thus inaccessible. Therefore, if you have a change of heart about staking your coins, require them for any reason, or notice a value increase that makes trading them a more favorable option, retrieving them won't be swift or simple — in fact, withdrawing them before the lockup period concludes can incur penalties.
3. Potential illiquidity of crypto token
A crypto platform's liquidity is determined by an asset's capacity to be converted into fiat money or other cryptocurrencies. If the investor takes a token with a small market capitalization, there can be a lack of liquidity, affecting the trade of the staking rewards afterward.
4. Crypto Theft
Crypto theft has increased alongside blockchain technology's popularity. Although some exchanges might claim that staked coins are secured in cold storage, sometimes that isn't the case. Technical faults and breaches can leave staked assets vulnerable, and investors can lose their funds and rewards.
5. Validator mistakes
As mentioned before, becoming a validator on your own is a highly technical and challenging task but also offers higher returns compared to staking pools and exchanges. However, if solo validators make mistakes during the validating process, they might not be rewarded at all, and staking won't be worth the labor.
Role of Crypto Staking for Blockchain Operations

Crypto staking plays a crucial role in blockchain networks, providing several benefits to both the network itself and its participants. Here's an overview of the importance of staking crypto in blockchain networks.
Security
Crypto staking enhances the security of blockchain networks by requiring token holders to have a financial stake in the system (staked funds). This discourages malicious behavior, as validators or stakers would risk losing their staked crypto assets if they act against the network's rules.
Decentralization
Crypto staking contributes to the decentralization of blockchain networks. By allowing a distributed set of participants with such assets to validate transactions and create new blocks, the control and influence over the network are distributed among a larger number of stakeholders, reducing the risk of centralization.
Consensus mechanism efficiency

Crypto staking is a key component of various consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanisms. These mechanisms enable more energy-efficient and scalable consensus compared to traditional Proof of Work (PoW) systems, as they don't require participants to solve complex mathematical problems to earn rewards.
Network governance

Cryptocurrency staking often comes with governance rights for token holders, allowing token holders with tokens staked to propose and vote on protocol upgrades, changes, or other decisions affecting the blockchain. In the case of DeFi staking, token holders with tokens staked can vote on changes in staking pools. This helps in achieving a more inclusive and democratic decision-making process within the community.
Incentives for participation

Cryptocurrency staking provides participants with incentives in the form of additional cryptocurrency rewards. By staking digital assets, users can earn a share of the network's transaction fees or newly minted coins. This incentivizes users to actively participate in securing and maintaining the blockchain network.
Liquidity and token economics
crypto staking contributes to the token economics of PoS blockchain platforms by reducing the circulating supply of the native cryptocurrency. This can potentially increase the scarcity and demand for the token, positively influencing its market value. Additionally, new tokens generated as staking rewards may be used to incentivize further network participation.
Upgradeability and flexibility
Some blockchain networks allow for the dynamic adjustment of staking parameters, such as the minimum stake of coins required or the reward distribution mechanism. This flexibility enables the blockchain network to adapt to changing conditions and ensures that the staking system remains effective and sustainable over time.
Economic security

Crypto staking provides economic security to the blockchain network by aligning the interests of those who stake crypto with the well-being of the blockchain. Those who stake tokens financially invest in the success and stability of the blockchain network, creating a strong economic incentive for them to act in its best interest.
In summary, staking is a fundamental mechanism that enhances the security, decentralization, and governance of blockchain networks. It aligns the economic interests of crypto investors with the overall health and success of the network, creating a more robust and sustainable ecosystem. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, staking is likely to remain a key element in shaping the future of decentralized networks and offer an increasing number of staking opportunities to crypto investors by allowing them not only to earn interest but participate in the validation process.
Protocol Staking: the Staking Process and Staking Rewards
In a protocol utilizing staking, validators are chosen to propose and validate new blocks or transactions. The selection process often depends on the amount of staked tokens a participant is willing to stake as collateral.
Crypto holders commit a certain amount of the native cryptocurrency of the blockchain protocol as collateral. This collateral in the form of staked tokens serves as a security measure, ensuring that validators have something to lose if they act maliciously or fail to perform their duties.
Validators operate network nodes, which are responsible for maintaining the blockchain and participating in the consensus process. They propose new blocks and validate transactions.
The probability of a validator being selected to create a new block or validate transactions is often proportional to the amount of native tokens they have staked. Higher stakes increase the chances of being chosen, providing an economic incentive for participants to stake more tokens.
Pooled Staking
Pooled staking, also known as staking pools or delegated staking, is a collaborative approach where multiple cryptocurrency investors combine their crypto investments to participate in a blockchain network's staking. This method allows individuals with smaller holdings to collectively contribute to the network's security and earn block rewards thus generating a source of passive income. Pooled staking is commonly associated with proof-of-stake (PoS) and delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS).
How investors pool their resources for staking crypto

A staking pool is created to bring together a group of individual investors interested in staking a particular cryptocurrency. The staking pool operates a validator node on the blockchain to validate transactions, and crypto users delegate their digital assets to the pool.
Delegating crypto funds does not transfer ownership but gives the pool more staking power and the right to use those tokens for staking purposes. The staking pool validator node actively participates in the blockchain network's consensus process. It proposes and validates blocks, and the staking rewards earned through cryptocurrency staking are distributed among the pool participants based on their delegated amounts.
Staking rewards, generated from activities such as block creation and transaction validation, are distributed proportionally among those who have staked tokens in the pool. The distribution is typically based on the amount of staked tokens each participant has delegated to the pool.
Liquid Staking
This staking type is an innovative concept that combines the benefits of staking in a blockchain network with a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. Such cryptocurrency staking is normally staking with liquidity, allowing token holders to participate in the DeFi staking process while maintaining the flexibility to trade or use their staked cryptocurrency holdings in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
In traditional staking, once crypto holdings are staked, they are often illiquid and locked for a specific staking period, and thus cannot be easily traded on crypto markets. This is connected with significant risk types such as counterparty risk, liquidity risk, and market risks. Liquid staking seeks to address this limitation.
Participants lock up their cryptocurrency tokens in a smart contract or a designated protocol of a staking platform to stake them on a PoS network. In return, they receive liquid or tradable tokens of the staking platform representing their staked position.
Staked tokens, representing the stalker's ownership in the staking pool, are issued to participants by the pool operator. These tokens can be freely traded or used in various DeFi applications while the underlying staked assets continue to contribute to the network's staking process.
Such assets are typically pooled together with the assets of other participants in a staking pool. The pooled assets collectively contribute to the network running on the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism.
Participants who hold such coins have the option to trade them on secondary markets or provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges. This enables them to access the value of their assets without having to unstake and wait for a lock-up period to end.
Liquid staked coins can be used as collateral in decentralized finance platforms, allowing participants to borrow or lend against their assets. This opens up opportunities for leveraging staked positions without sacrificing the benefits of staking work.
This staking type allows participants to unstake and access their coins at any time if we speak about soft staking, or after a specific staking period in the case of cold staking. This flexibility contrasts with traditional staking, where there might be lock-up periods or delays in withdrawing staked tokens.
Platforms offering staking services also normally offer an option for a lucrative passive income. We can compare staking on a reliable platform with a good savings account to which you have access at any moment. Staking can diversify your crypto portfolio significantly and help you to maximize rewards.
Delegated Staking

This staking type is also known as delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), is a type of proof-of-stake consensus mechanism employed by certain blockchain networks to achieve distributed consensus and secure the network.
DPoS is a variation of the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, where token holders (delegators) vote for a limited number of delegates (validators) who are responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks. This is one of the types of staking that aims to improve scalability and energy efficiency while maintaining a decentralized network.
Comparative Analysis of Staking Types
Let's compare some of the common staking types in the cryptocurrency space.
Proof of Stake
Key Features:
- Validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to lock up.
- Participants earn block rewards in proportion to their staked amount.
- Generally more energy-efficient compared to proof-of-work (PoW) because no crypto mining is involved.
- Examples include Tezos, Cardano, and Algorand.
Advantages:
- Energy efficiency.
- Decentralization based on token ownership.
- Lower barriers to entry for participants.
Drawbacks:
- Potential centralization if wealth distribution is uneven.
- Security risks if a large number of tokens are controlled by a small number of entities.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Key Features:
- Delegates are elected by token holders through a voting process.
- A small number of elected delegates often lead to faster consensus and increased scalability.
- Examples include EOS, Tron, and Lisk.
Advantages:
- High scalability and faster transaction confirmation.
- Community governance through voting.
- Potential for more efficient decision-making.
Drawbacks:
- Potential centralization if a small number of entities control a significant portion of tokens.
- Voter apathy if a large portion of token holders does not actively participate in the voting process.
Liquid Staking:
Key Features:
- Staked coins are tokenized, providing liquidity.
- Participants can trade or use their staked crypto in various financial applications.
- Examples include projects working on tokenized staking solutions.
Advantages:
- Enhanced liquidity for coins.
- Flexibility to trade or use coins in DeFi.
Drawbacks:
- Protocol and smart contract risks associated with tokenization.
- Trade-offs between staking rewards and liquidity.
Overall Considerations
PoS and DPoS aim to achieve decentralization, but the level of decentralization can vary. Liquid staking and masternodes may introduce additional centralization risks.
DPoS is often praised for its scalability, while PoS and masternodes may have varying degrees of scalability.
PoS and DPoS are generally more energy-efficient compared to PoW.
In summary, the choice of staking type depends on specific project goals, network requirements, and the preferences of the community. Each type comes with its advantages and challenges, and the suitability of a particular mechanism depends on the goals and design philosophy of the blockchain project.
Choosing the Right Staking Method
Choosing the right method to stake depends on various factors, including your investment goals, risk tolerance, technical expertise, whether you want to have access to trading coins, and preferences. Here are some considerations to help you decide on the most suitable method to pick among all types of staking the best option.
Investment goals
If your goal is to hold and accumulate a particular cryptocurrency for the long term, traditional Proof of Stake (PoS) or Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) might be suitable. These methods provide a way to earn additional tokens over time.
If you are looking for liquidity and the flexibility to trade or use your staked assets, liquid staking or staking solutions with tokenization features may be more appropriate.
Risk tolerance
If you have a lower risk tolerance, consider traditional staking services such as PoS or DPoS. These methods generally involve less complexity and offer a more predictable staking experience.
If you are open to higher risk for potentially higher returns, exploring a liquid option or staking coins in projects with innovative features may be appealing. However, be aware of the additional risks associated with newer technologies.
Project and network considerations
Thoroughly research the specific projects and networks you are interested in. Understand the consensus mechanism, governance structure, and overall goals of the blockchain. Different staking methods may align better with the project's objectives.
Liquidity preferences
If liquidity is a priority, consider those staking methods that allow you to tokenize your staked assets or use them, providing the flexibility to trade or use them in DeFi applications.
Return on investment of staked tokens
Consider your yield expectations and the potential return on investment. Different staking methods may offer varying levels of rewards, and understanding the reward structure is crucial.
FAQ
Is it safe to stake crypto?
As in any other crypto-related service, the safety of crypto staking depends on the exchange or stake pool you choose to complete your staking process. For example, some platforms penalize validator nodes if they don't uphold 100% uptime or include fake transactions into the blockchain. Choose a platform that has precise security mechanisms.
Can I lose money staking crypto?
There is a possibility that asset value will decrease fast, impacting the interest earned from staking paid in the same currency. Therefore, you should analyze the volatility of the crypto coin before staking it.
What is the difference between crypto staking and farming?
Both investing methods require holding coins for some time to make a profit. However, staking makes investors lock up their crypto assets, being less risky and having a more stable return rate. On the other hand, farming requires that investors deposit crypto in early-stage liquidity pools, being riskier but presenting higher short-term returns.
How does NFT staking work?
NFT staking uses the same system as crypto staking: you need to lock up NFTs to earn revenue based on annual percentage yield while preserving the ownership. However, not every NFT can be staked, so investors need to check if staking is one of the asset's features before acquiring it.
Is staking on crypto worth it?
In short words - yes. Crypto investors can earn rewards just holding (staking) their crypto tokens and the rewards are added to the staking pool. The most crypto projects like exchange platforms and crypto launchpads offer to stake tokens for regular or irregular schedules.
Would you like to start investing in the most promising crypto projects? Learn how to invest with BullPerks, the fairest and most community-oriented decentralized VC and multichain launchpad!
Disclaimer. This material should not be construed as a basis for making investment decisions or as a recommendation to participate in investment transactions. Trading digital assets may involve significant risks and can result in the loss of invested capital. Therefore, you must ensure that you fully understand the risk involved, consider your level of experience, investment objectives, and seek independent financial advice if necessary.